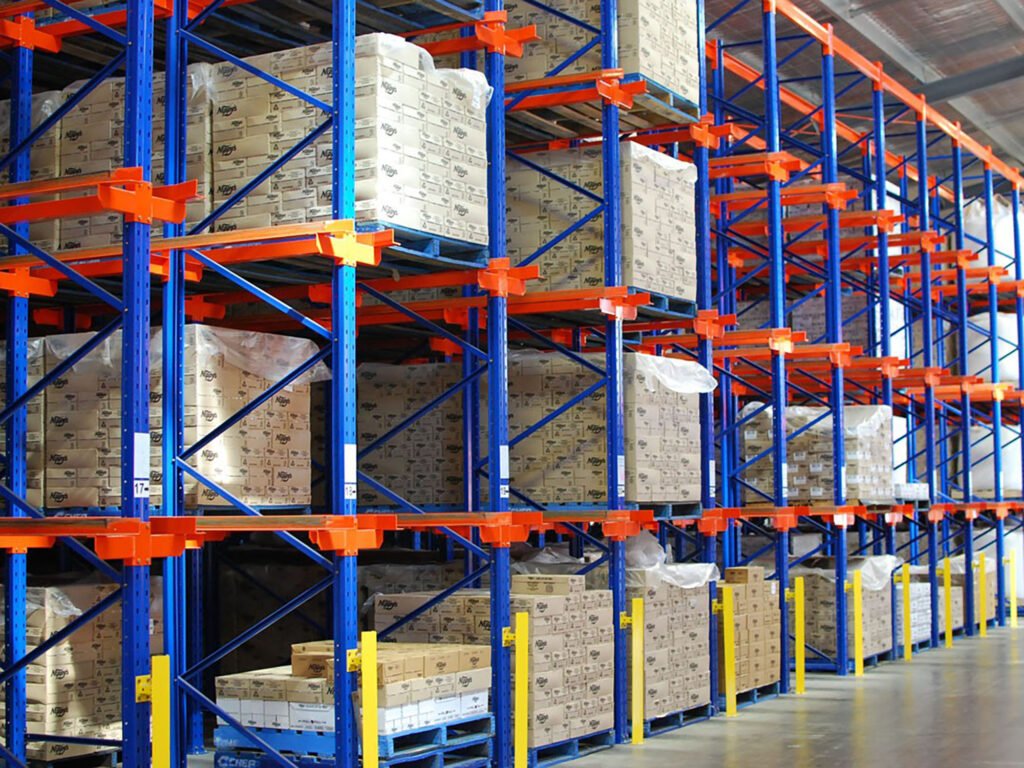
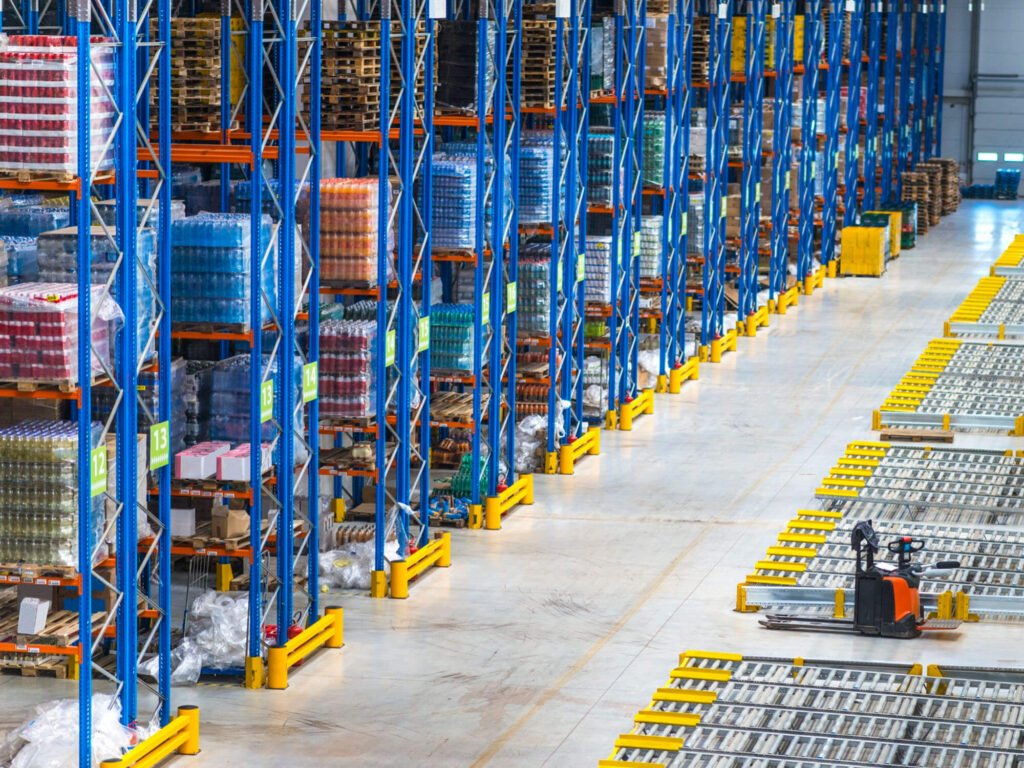
As a high-density storage system, the drive-in racking system design helps optimize warehouse space and height while reducing forklift operating lanes. Its modular construction facilitates simple assembly and maintenance, making it an effective warehouse storage solution.
In addition, drive-in pallet racks are also popular across the world, from China to the United States, thanks to their affordable cost. However, in order to pick the right drive-in racking system design for your warehouse, you need to thoroughly understand this storage configuration.
This in-depth guide will walk you through everything there is to know about the drive-in racking solution, including its exact definition, structure, and the optimal way to work with it. You’ll also explore the essential considerations to help you finalize your selection more quickly and effectively.
What Exactly Is A Drive-In Racking System?
The drive-in racking system design is a compact, high-density storage solution that optimizes warehouse space by reducing the number of forklift working channels. This system enables forklifts to drive straight into storage lanes, allowing for deep stacking of pallets using the LIFO method.
Drive-in systems comprise pre-assembled racks with inner lanes created by joining sets of frames and vertical uprights. Upper longitudinal beams, horizontal braces, and forklift guide rails are some of the design’s key components that work together to provide a robust structure.
Drive-in racking systems typically support GMA pallets with a standard dimension of 48 inches long by 40 inches wide. In order to maximize storage density, the common height for this racking design usually ranges from 16 to 20 inches, though these racks can be modified to fit varied facility sizes.
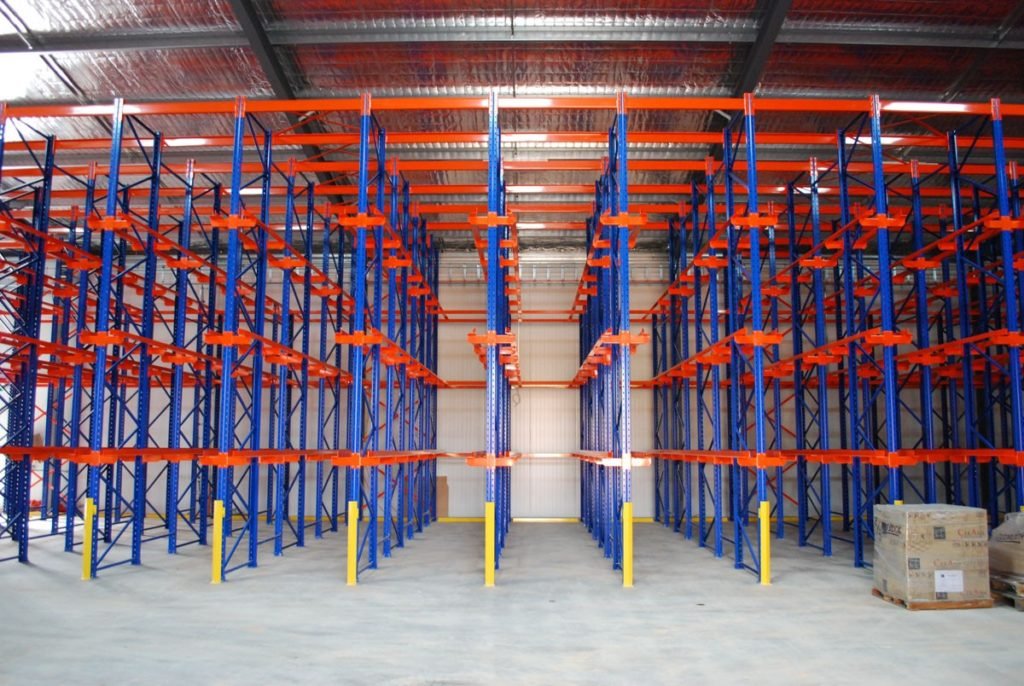

Benefits Of A Drive-In Racking System
If you want to know why many warehouse managers love drive-in racks, take a look at their long list of benefits. The following are some of the main advantages:
- Enhancing storage density: This racking design provides a better storage density than classic selective pallet racks as it stores pallets closer together and with fewer lanes. This is achievable because the system needs only one lane for retrieval, as opposed to two aisles in a standard pallet racking solution.
- Augmenting inventory management: Drive-in racks also offer transparent logistics management with complete control over inventory, traffic, and workflow, thereby increasing total warehouse efficiency.
- Highly cost-effective: With increased storage density and better use of warehouse floor space, the drive-in racking system design is surely a cost-effective solution. The cherry on top is that you can tailor it to your company’s exact requirements.
- Allowing customizations: What makes drive-in racks so appealing is their customization. You can easily reconfigure this system to meet your various storage demands, such as turning it into a drive-through rack or featuring inclined shelves to enable pallets to travel down to the front for loading and unloading.
- Facilitating easy assembly: Thanks to the modular structure, the drive-in racking solution is simple to build, relocate, and upgrade. It also needs minimal effort for maintenance and upkeep, thus saving on installation and labor.
- Coming with numerous safety components: You’ll understand more about this benefit after learning about the drive-in racks’ construction. But for now, you can remember that the drive-in systems offer a wide range of safety elements, such as upright protections and forklift guide rails, to safeguard the structure.
Drawbacks Of A Drive-In Racking System
Every coin has two sides, and so does the drive-in racking system. Beside the aforementioned advantages, this inventory design also contains certain drawbacks, making it not well-suited for all product types or storage settings. Let’s address some of them below:
- Posing higher collision risks: Due to the large traffic volume of forklift activities into and out of the drive-in racking system, collisions with the structure become more frequent. Thus, forklift operators must attend driving courses or at least get familiar with the new system.
- Creating dead inventory space: Also known as “honeycombing”, this negative impact often occurs when forklifts fail to reach the rear of the racking system to place goods, which results in dead storage space.
- Limiting goods accessibility: As the drive-in solution facilitates the LIFO method, meaning the last items to enter the system will be the first ones to leave, it can be difficult to access items deep inside the structure (those that have entered the system for a long time).
Main Applications Of A Drive-In Racking System
After exploring the pros and cons of the drive-in racking system design, it’s easier to understand how you should utilize this inventory solution. This part will help you organize those ideas systematically. Here are certain situations where you should employ drive-in racks:
- Having limited available space: When you have a small warehouse, it’s wise to deploy drive-in racks, as these solutions help you optimize inventory space, meaning you can stock more items in the same footprint.
- Storing homogeneous items: For those who need to hold large quantities of pallets of the same products with low turnover rates, drive-in racks are the go-to solution. They are especially effective with non-perishable items due to their compatibility with the LIFO approach.
- Not prioritizing direct access: As the drive-in racking system reduces access to certain pallets located deep inside the structure, it can be useful in case you don’t consider direct access a deal-breaker.
With the above pointers, drive-in racks are ideal for various industries that require less aisle space, including food and beverage, manufacturing, pharmacy, cosmetics, and electronics.
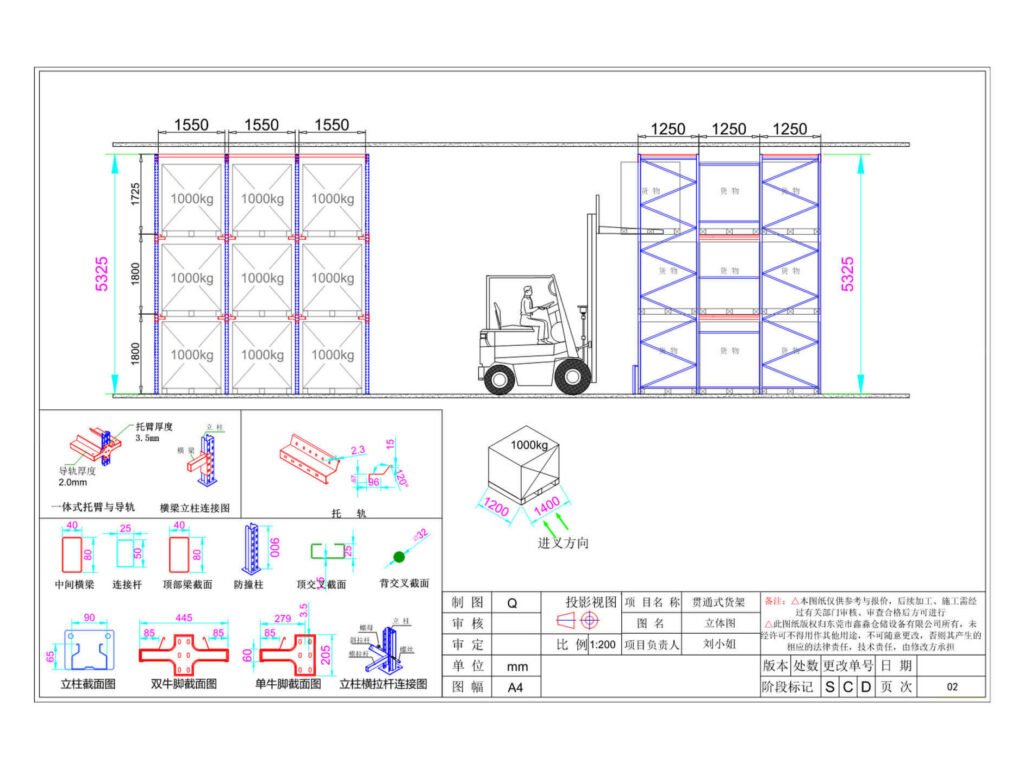
Exploring Drive-In Racking System Design’s Components
Now that you’re familiar with the drive-in racking system design, it’s time to discover the essential components that make up this storage solution. Here is a short list of key elements you need to know about drive-in racks:
- Frames: This element is one of the key components of drive-in racks. Typically, frames are made up of two uprights, base plates, and anchoring parts.
- Uprights: These galvanized components are the frame’s major pieces. Clients can browse numerous upright options to meet their unique warehousing demands.
- Upper longitudinal beams: These beams connect the frames in the top region crosswise, thereby reducing the structure with gantries. They are a must-have element in all of the compact racking aisles.
- Horizontal braces: You can easily find these metal pieces situated on top of the drive-in design. Their ultimate role is to strengthen the solution’s compact structure.
- Forklift guide rails: Often spanning the length of the aisles, these floor-level steel rails are designed to guide the forklift as it enters the drive-in inner structure and protect it from potential collisions. They also help remove the forklift from the drive-in racks more easily.
- Frame and upright protectors: As the name suggests, these protectors safeguard the inventory system against forklift impacts that can cause damage to the frames and uprights.
- Welded base plates: The main purpose of these elements is to reinforce the drive-in frames, ensuring that they can withstand their intended maximum load capacity.
- Brackets: Often fastened to the uprights, brackets help hold up the pallet beams and support rails on different levels of the drive-in structure.
- Pallet beams and support rails: Unlike brackets, these metal horizontal profiles support the pallets at each level of the drive-in racking system design. Oftentimes, they are attached perpendicularly to the upright using brackets.
- Pallet guidance: Located at the front pallet beam, this part helps assist forklift operators during their loading and unloading of products. It’s also a crucial element that shields the drive-in racks from potential impacts.
- Pallet backstops: Designed as preventive safety components, the primary role of pallet backstops is to keep pallets from falling at the rear of the aisle due to improper forklift movement and handling.
Best Practices To Work With A Drive-In Racking System
Parallel lanes inside the structure enable forklifts to circulate during loading and unloading pallets. Each lane is allocated to a single product reference, allowing for optimal stock management in the warehouse. Here are some optimal ways to utilize your drive-in racking system in order to maximize its advantage.
Forklift drivers can carry pallets onto the support rails on both sides of each level. One best practice is to load the pallets at a slightly greater height than the ultimate location to guarantee secure and efficient placement.
Another best practice relates to the sole entrance of drive-in racks. Forklifts have to drive into the structure to deposit items in the rear, piling newer products in front of older ones. Although this configuration requires more time to handle the products, it facilitates tight packing, which is useful in storage units with limited space.
Drive-In Vs Drive-Through: A Detailed Matchup
Drive-in vs drive-through is one of the most talked-about matchups when it comes to warehouse racking configurations. Despite their quite similar names and designs, they have unique characteristics and serve distinct purposes. This part will compare these two racking systems using a set of criteria:
- Number of entrances: The drive-in solution has just one entry for loading and unloading pallets. Forklifts can only reach the storage lanes from one side. On the other hand, drive-through racks possess two openings, which enable forklifts to load from one end and discharge from the other.
- Forklift operation: It’s more challenging for forklifts to access drive-in racks, as the vehicle must drive backwards to exit the structure. However, the drive-through system makes loading and unloading pallets inside the racks simpler and faster, as forklifts can reach pallets from either end.
- Applicable inventory management method: This is another distinction between the two racking designs. Drive-in racks operate on the LIFO principle, making them ideal for low-turnover inventory. Yet, their counterparts use the FIFO approach, which is perfect for high-turnover products.
- Well-suited applications: The drive-in racking system design works well with facilities that prioritize space efficiency above product rotation. On the other hand, drive-through racks are ideal for warehouses that need quick stock rotation and high turnover rates.
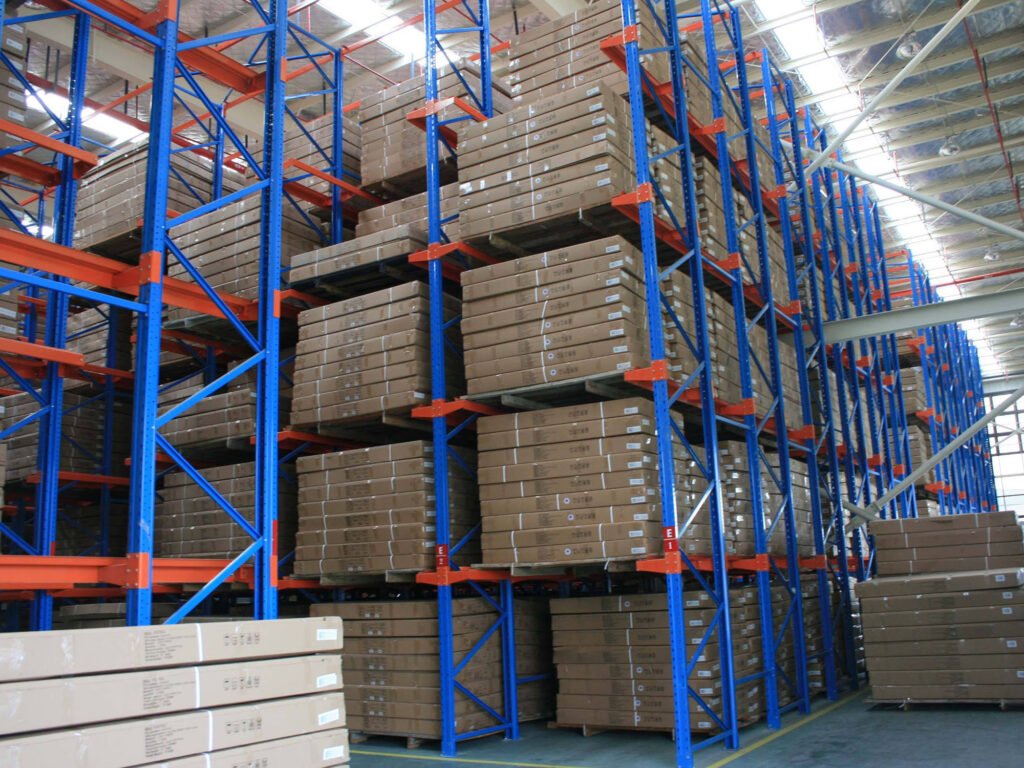

Estimating The Cost Of Drive-In Racking System Design
Speaking of cost factors, let’s dive deeper into this subject. The expense of a drive-in racking system design depends on a set of features, including the racking materials, the number of pallets required, freight, and installation services.
In addition, you’ll need to account for other aspects, like the maximum weight of your pallets and the depth of your structure. Although drive-in racks require minimal maintenance, it’s essential to consider the upkeep expense as well.
Key Factors To Assess When Choosing A Drive-In Racking System Design
It’s clear now that the drive-in racking system can handle large amounts of homogeneous items. However, to assess the efficiency and suitability of this storage solution, you’ll need to go over the following key factors:
#1: Warehouse’s Size And Height
Often occupying 4 feet wide and 3–8 feet deep, drive-in racks are best suited for warehouses that are large and tall. The height of your inventory facility should span from 10 feet to 20 feet in order to benefit from the drive-in racking system design. This design enables deep stacking of up to 10 to 12 pallets deep and 7 pallets high.
Smaller warehouses, particularly those that store things in cartons, may not need such high-density storage. Only consider drive-in racks when your facility holds a large number of palletized goods due to their effective use of space, which increases total storage capacity.
#2: Material Handling Equipment Type
An efficient warehouse should have material handling equipment to handle the lifting and stacking of palletized items. This also applies to facilities using drive-in racks. Forklifts are the most popular option, but there are more choices you can consider. Let’s explore some types of material handling equipment below:
- Forklifts: These vehicles are industrial tools that transfer pallets and other products around the warehouse. Forklifts are either powered by a motor or electricity. Their lifting mechanism is critical for efficient warehouse operations.
- Pallet jacks: If you need a vehicle to transport pallets over short distances, consider pallet jacks, which are the most basic sort of forklift. You can find hand-powered jacks for moving lightweight items. However, there are also motorized pallet jacks, or walkies, that help with heavier pallets.
- Side loaders: Warehouse operators often control side loaders in a separate compartment. Due to the drive-in racking system design, these vehicles are less efficient than forklifts when used.
- Counterbalance forklifts: Thanks to the additional counterweights, counterbalance forklifts are more stable during operations. They maneuver through drive-in racking aisles, easily accessing all pallets. Their low center of gravity helps them glide through confined places with ease.
#3: FIFO Vs LIFO
Regarding inventory management methods, there are only two options. You either choose FIFO or opt for LIFO. The choice really depends on your stored products and their characteristics. If you prefer LIFO, congratulations, as drive-in racks are designed to accommodate that method. Let’s talk a bit more about both approaches.
- LIFO: This inventory management strategy prioritizes the most recently added goods for shipping. It’s great for non-perishable commodities since it allows firms to easily maintain inventory and reduce storage expenses. This technique works ideally with the drive-in setup.
- FIFO: Adhering to the “first in, first out” concept, FIFO ensures that the oldest inventory gets shipped first. This strategy lowers waste and obsolescence, preserves product quality, and increases efficiency by cycling inventory on a regular basis, making it suitable for perishable items. If you select FIFO, make sure to use drive-through racks instead of their drive-in siblings.
#4: Standard Pallet Dimensions
When choosing a drive-in racking solution for your warehouse, it’s critical to consider pallet sizes in order to maximize storage efficiency and system compatibility. The standard pallet size (48 inches long by 40 inches wide) determines the distance between rack components, ensuring that pallets fit securely without causing damage.
Typically, drive-in racks are intended to accommodate pallets that are 6 feet high and weigh around 38 to 48 pounds. Also, ensure that the weight capacity of your pallets (often 4,000 pounds) matches the rack’s load-bearing criteria.
Conclusion
In conclusion, deploying an appropriate drive-in racking system design is critical for increasing warehouse efficiency and storage capacity. Understanding the system’s components and functionality allows you to modify the design to meet your individual requirements, guaranteeing optimal use of space and resources.
When selecting a drive-in racking system design, make sure to consider many aspects, such as your warehouse size and height, pallet dimensions, forklift types, and inventory management approaches, to land the most suitable option.
By following the key ideas and best practices outlined in this guide, you can easily reach the high-density storage solution that suits your operating needs and budget, thereby resulting in a more streamlined and efficient warehouse environment.




