In warehousing and logistics, understanding standard racking sizes is crucial for efficient storage solutions. This article will provide information on pallet racking standard dimensions and other essential aspects of warehouse racking dimensions that facility managers should be aware.
Understanding Standard Racking Systems
The foundation of any efficient warehouse lies in its racking system. Standard racking provides materials handling systems that comprise the existing storage facilities which are designed to provide both accessibility, storage capacity, and flexibility. Let us introduce the concept of standard racking and its background which gives an understanding of why this type of warehouse has gained so much popularity around the world.
What is Standard Racking?
Selective racking or standard racking is one of the oldest and most widely used forms of storage racking across the globe and is prevalently used in warehouses and distribution centers. Upright frames and horizontal beams that create skeletal structures with high riser capacities of palletized stocks are major components of it. The key factors which contribute to the wide use of standard pallet racking include its multi-functionality, reasonable price, and availability of storing pallets.

The Importance of Standardization
Standardization in racking systems is crucial for several reasons:
- Interchangeability of components: Standard parts can also be easily swapped or shifted from one section of the warehouse to another section.
- Consistency in storage capacity calculations: As the dimensions are standardized it can help in making a perfect planning and calculation of the allotted storage capacity.
- Easier compliance with safety regulations: Standard designs are sometimes referred to the safe and standard measure that existed where safety requirements are concerned.
- Simplified training for warehouse staff: In situations where systems have to be implemented, it becomes easier to train as everyone gets to conform to certain standards.
- More efficient procurement and maintenance processes: This way all the needed supplies can be bought at once and the servicing practices also do not vary from one device to another.
If a business follows the proper warehouse racking standards, it will mean that the kind of storage systems that are put in place are both efficient and safe. It also makes possible faster rearrangement and adjustments of the format of the warehouse according to the dynamism of business operations.
Standard Racking Sizes: A Comprehensive Overview
Generally, it will be apparent that it is critical to comprehend the diverse sizes and proportions that are related to standard racking, to strategic warehouse and space planning efficiently. This section will analyze the typical elements that are inherent in a conventional racking installation and illustrate the most frequent dimensions used in the warehouse environment.
Upright Frame Dimensions
Upright frames are the vertical components of the racking system. Standard sizes for upright frames typically include:
- Height: 8 feet to 40 feet (2.4 meters to 12.2 meters)
- Depth: 24 inches to 48 inches (61 cm to 122 cm)
Several aspects when deciding on the dimensions of the upright frame include the ceiling height, floor space, and load bearing.
Beam Lengths
Beams are the members running horizontally on the upright frames and they are directly involved with the bearing of the pallets. Decisions pertaining to beam length are particularly important since they help to determine the number of pallets that can fit into each bay. Common standard racking beam lengths include:
- 8 feet (2.4 meters)
- 9 feet (2.7 meters)
- 10 feet (3 meters)
- 12 feet (3.7 meters)
Beam lengths are typically chosen based on:
- The size of the pallets being stored
- The ideal pallet placement per bay
- The overall layout of the warehouse
Beam lengths depend on the size of the pallets stored and the number of pallets per bay.

Bay Configurations
A bay is the space between two upright frames, defined by the beams that connect them. These bays are a major feature of any warehouse and their layout defines the overall storage capacity as well as the efficiency of the warehouse. Standard bay configurations in standard pallet racking systems often include:
Single-deep: One pallet deep, that provides complete selectivity.
Double-deep: Piling the pallets twice higher, enhances the pallet density at the price of some accessibility
Drive-in/Drive-through: Several pallets high when product is standardized for both to increase storage space.
The choice of bay configuration depends on several factors:
- Inventory turnover rates
- Storage density requirements
- Accessibility needs
- Types of products stored
- Material handling equipment available
Every configuration suggests a unique degree of storage capacity and adjustment and provides the warehouse managers with the opportunity to implement the most suitable racking system.
Pallet Sizes and Their Impact on Racking Design
The design of any standard racking system is inherently related to the size and kind of pallets it has to contain. Being aware of the interconnection between pallet size and choice of racking is essential for the creation of effective and secure pallet storage.
Standard Pallet Dimensions: It is vital to consider the standard pallet sizes in the design of a standard racking system to be used. Common pallet dimensions include:
- North American (GMA) pallet: 48 inches x 40 inches (122 cm x 102 cm)
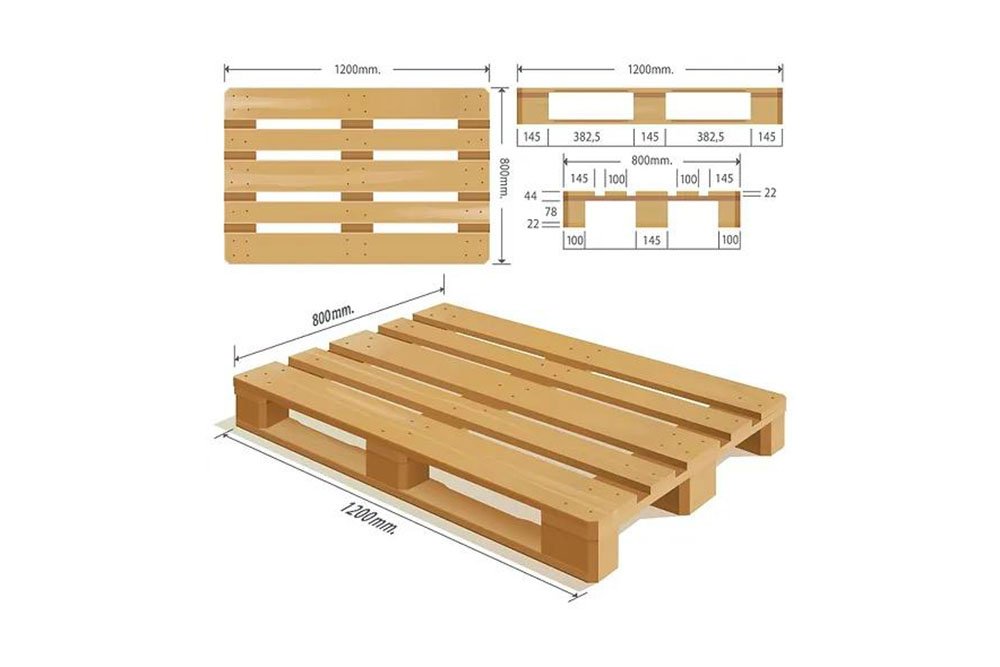
- Euro pallet: 1200 mm x 800 mm (47.2 inches x 31.5 inches)
- Australian pallet: 1165 mm x 1165 mm (45.9 inches x 45.9 inches)
Clearance Requirements: When designing a standard pallet racking system, it’s essential to consider clearance requirements:
- Vertical clearance: Typically 6 inches (15 cm) above the pallet load
- Horizontal clearance: Usually 3 inches (7.6 cm) on each side of the pallet
Clearance plays an important role in pallet storage and retrieval processes, where pallets are placed and retrieved at an optimal distance and manner.
Warehouse Racking Standards and Regulations
Ensuring the safety and efficiency of warehouse operations goes beyond just selecting the right sizes and configurations. There is a need to adhere to set standards and codes relating to design, installation and maintenance of the racking system.
Safety Standards
Warehouse racking standards are governed by various organizations and regulations, including:
- ANSI (American National Standards Institute)
- RMI (Rack Manufacturers Institute)
- OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration)
- EN 15512 (European Standard for Steel Static Storage Systems)
These standards cover aspects such as:
- Load capacity calculations
- Seismic design requirements
- Installation procedures
- Inspection and maintenance protocols
Load Capacity Considerations
Understanding load capacity is crucial for safe standard racking design:
- Beam capacity: The maximum weight each beam pair is able to take
- Upright capacity: How much load an upright frame can take is also another important factor.
- Bay capacity: The overall weight limit of all the levels in a bay it an individual
Calculations and compliance of these capacities should be made in the right manner for the safety concerns of a warehouse to be observed.
Maintaining and Inspecting Standard Racking Systems
Standard racking system require proper maintenance and inspection in order to enhance workplace safety, and productivity and meet the set safety standards. Besides, a good racking system has the potential to last longer than its counterparts, in addition to the reduced incidence of accidents and destruction of stocks.
Regular Inspection Protocols
Carrying our regular check-ups and inspections goes a long way in reducing problems to the minimum. This ranges from checking by the operators on a daily basis, checking by supervisors on a weekly basis, and checking by a qualified person on a yearly basis. Routine checks include daily and weekly checks during which you look for signs of damages or misalignments, more detailed checks are done during annual checks and can include load testing if necessary.
Common Issues and Remedies
Some of the racking issues that need consideration by the managers include damaged components, missing or loose safety locks, overloading, and misaligned racking structures. If some of the parts are broken, they should be replaced immediately; locks that are loose will need to be tightened; bays that have too much load will need a redistribution of the load; and the frames if not well aligned will need to be adjusted or even re-installed by professionals. Constant evaluation and prevention of the above-discussed problems ensures that the warehouse is safe and efficient.

Choosing the Right Standard Racking System for Your Warehouse
Choosing the right standard racking system is a very important decision process that affects the functionality of the warehouses. This section seek to give a guideline on how one can evaluate his or her needs and collaborate with the suppliers to arrive at the most suitable solution.
Assessing Your Needs
Consider the following factors:
- Properties of stock (size, weight, turnover rate).
- Dimensions of the given area including the floor area and the ceiling height.
- Material handling equipment
- Budget constraints
- Future growth projections
Working with Racking Suppliers
When selecting a supplier:
- Check their compliance with the set warehouse racking conventions
- The material should include detailed CAD layouts and 3d visualizations
- Make sure that they provide installation and maintenance services.
- Look for additional features to address certain requirements
Conclusion
Standard racking systems are the backbone of efficient warehouse operations. Having learned the various possibilities of standard pallet racking sizes, following the warehouse racking standards, and integrating sophisticated tools, the businesses can enhance the efficiency as well as safety of the storage systems. Over time, changes in the industry will continue to emerge and thus it will be important to be acquainted with new innovations in racking technology and other related issues in the market.
The various ideas about the effectiveness of the racking systems should be understood with reference to the fact that the success of the warehouse does not only depend on the choice of the appropriate racking system but also on the ability to optimize this system taking into account the requirements of the company and the peculiarities of its activity. Taking all the following factors into consideration when choosing standard racking sizes and systems will enhance a better storage solution for your business in the future.




